LIC- India
India and especially kerala was the first developing nation to launch a national family planning programme as early as 1952 not only have they encouraged the use of contraception but have included many social changes such as healthcare and education the family planning consisted of educating families on how many children they should have and also the use of contraception, this would be through education, this scheme has been very successful for india, in 2009 the use of contraception has tripled compared to the use of contraception in the 1960s, however only 3% of contraceptive methods were condoms this shows that women are getting the choice of not having children because their partner and themselves have been educated.
These are some of the things India has done to control its population.
● improving education standards and treating girls as equals to boys
● providing adult literacy classes in towns and villages
● educating people to understand the benefits of smaller families
● reducing infant mortality so people no longer need to have so many children
● improving child health through vaccination programmes
● providing free contraception and advice
● encouraging a higher age of marriage
● allowing maternity leave for the first two babies only
● providing extra retirement benefits for those who have smaller families
● following a land reform programme (land redistributed so that no-one was landless, no family was allowed more than 8ha and everyone could be self-sufficient)
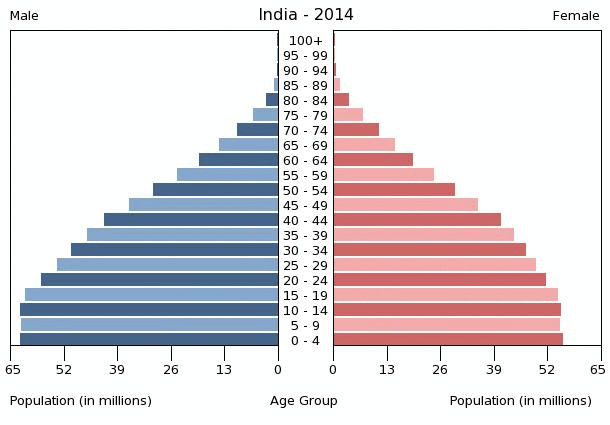
Because of the family planning working well fertility rate has been drastically reduced however compared to most of the western world it's still high, the fertility rate has fallen but it's still not at replacement level (being 2.1) in 2012 India's fertility rate was 2.50 compared to japan's 1.41(2012)
however as you can see in the picture its fertility rate has been dropping, From 5.7 in 1966, it declined to 3.3 by 1997 and 2.7 in 2009 and only dropping 0.2 by 2012 now its rate of decline is very slow and people believe that it's only a matter of time till it passes China in the world largest population.
The Indian government has not only been trying to reduce fertility rate but it has also introduced five- and seven-year plans to improve agriculture. Land reform policies have been introduced in an attempt to share the land more evenly. Over 160 million people live on farms smaller than 1 hectare, the minimum size required to support an Indian family. Almost as many own no land at all. Land reform concentrated on redistributing land to landless peasant with varying success.
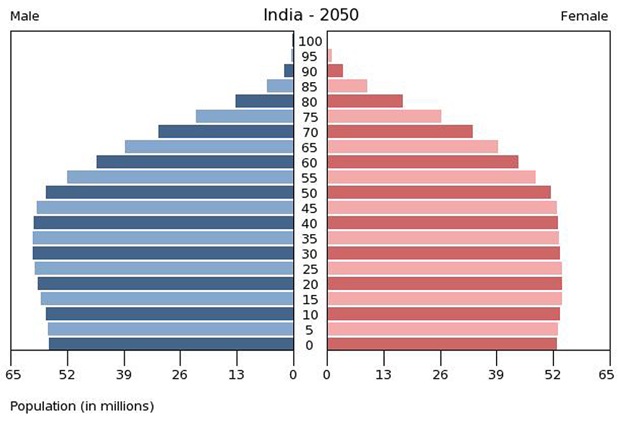
So if the land reform process works which it is then it will raise a huge amount of people above the poverty line ($1.25) in 2015 29.8% (360 million) of India's 1.21 billion people live below the poverty line this is, a sharp drop from 37.2% in 2004-2005 as long as this drop is sustained india will eventually increase its GDP and lead to increased life expectancy THEN we will see a huge increase in population with india's life expectancy being 66 years old it will easily increase to 80+ this leaves a possible 20 million extra people in india.
India literacy rate is still very low 78% and for women, it's only at 65.46% this compared to males 82.14% so without this improving then there fertility rate of women their population can never get to the rate they want.
India's total land mass is 3,287,240 km squared 54% of this is used for agriculture unlike many countries India has very habitable land that's why so much is used for crops, only a few regions are uninhabitable because of the damage the monsoon season does however with development India will surely develop ways to counter the damage is does this will allow it to make space for infrastructure houses India's total population only and it has a total population of 1.252,000,000,000 that's 1.252 billion.
India's in stage 3 of the dtm (demographic transition model) this means” death rates are low and birth rates decrease, usually as a result of improved economic conditions, an increase in women’s status and education, and access to contraception.” quote from https://www.populationeducation.org
India has a very poor health system not only that but it has barely any accessible roads to hospitals and the majority of hospitals are shelters and tents set up in rural places if you are ill you have to walk, in some of its most developed cities there is an option for ambulances but with congestion so bad there is no point in getting an ambulance, in 2012 there were 1.7 nurses per 1000 people in india so the chance of seting a free space or to be treated to on time is very small this compared to japan's 11.5 nurses per 1000 people.
In India there are a huge amount of people leaving the country with a total net migration of -2,294,049 with most of the people moving originated from the north could this mean that there is a lower standard of living there? well yes there is crime rate is rising and with the mountains terrain life there must be very hard, ontop of this there has been a huge amount of earthquakes in the last few decades.
HIC- japan
Japan is also interestingly rated 10th in the world by population count and has a total landmass of about 377,835 km²( Japan has nearly double the population of the UK but with only a land mass 1.5 times bigger) however most of this area is uninhabitable as it consists of tiny islands and mountainous terrain this is what makes it strange as almost four-fifths of Japan is covered with mountains. The Japanese Alps run down the center of the largest island, Honshu the highest peak is Mount Fuji, a cone-shaped volcano.
So for it to have such a high population being a total of 127.3 million (2013) 21% of these people being over 65 years old it's no wonder its population density is so high in its cities as that where everyone lives with a population density , of 336 people per square mile most of the people are crammed into its main cities especially in the south, these main cities being :toyoko with a Metropolitan area population of a huge 32 million and a citie population of 13 million toyoko having an area of 6,993 square kilometers, the area of Tokyo is 0.6% of the total area of Japan but it holds 10% of its total population (working off its city population) it also has a population density of 4,750 persons per square kilometer.

The total migration between Toyoko is 186,000 people came into Tokyo while 172,000 moved out, this gives a net migration of 14,000 per year and Yokohama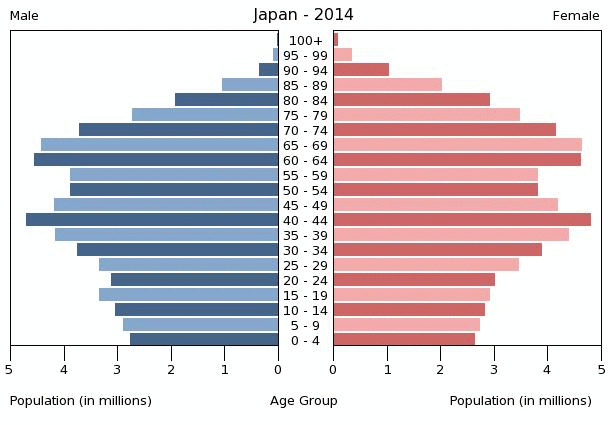 (south of Tokyo) with a total population of 3,689,603.
(south of Tokyo) with a total population of 3,689,603.
 (south of Tokyo) with a total population of 3,689,603.
(south of Tokyo) with a total population of 3,689,603.
Japan has 1 mega cities this is Tokyo, compared to India's number of megacities being 0! however with the huge amount of people in slum areas it's hard to really distinguish its true population , India also has a population density of 436 on 2014 this is amazing as India is approximately 8 times larger than Japan, however, it still maintains a high density, unlike Japan only a small amount of India is uninhabitable.
In Japan 80% of birth control methods are condoms whereas in India this is only 3% while the rest use either the rhythm method or a spermicide jelly a huge 1 in 5 people use the rhythm method this goes back to Japan's culture and purity beliefs and that the majority of people in Japan are Buddhists which are against any form of contraception. these are reasonably expensive methods, amazingly japan is against permanent methods of contraception taken from factsanddetails.com “Abortions were banned in 1907 and all kinds of birth control were made illegal in World War II. In the 1950s, when the population was growing rapidly and women were added in the labour force, abortion was legalized for "economic and health" reasons.” so the main reasons for Japan's fertility rate being so slow is because social and political changes and propaganda is very strong.
Japan's natural increase is at -1.73% this is very low compared to India's natural increase of 13.69%
● High GDP - Gross Domestic Product
● 210 doctors per 1000 people
● Women having children older
● High quality of life
● Very strict immigration policies
● Average age of first marriage increasing
● Marriage rates are falling
● Higher proportion of women in employment
All these points are reasons for women not to have children in some way or another this and the fact that it's so overpopulated, what also is not helping japan's ageing population crisis is the fact that immigration is very strict even more so than Australia and like Australia legal immigration has become restricted to skilled workers and so most of the immigrants are skilled professional people employed by large corporations such as Mitsubishi and Toyota Motor. However around 200,000 illegal foreigners can be found in Japan, most of whom are Chinese, there is not only a lack of skilled workers but a recent survey has shown that low skilled workers are also needed in Japan.
Japan's workforce is at 65,559,495 that's just over 50% of people working, however japan's life expectancy is at 84 years old compared to India 68 years old life expectancy, this is a huge difference and could be linked to many things such as japan's amazing health care and its monthly wage at $669 compared to India's yearly wage of $616
The country’s labour force began to shrink in the mid-1990s, and the total population peaked in 2008. If nothing changes, there will be 30m fewer Japanese by 2050, and by the early 2100s, the population could be half or even a third what it is today if it carries on to not letting people into their countries.
Also, Japan is situated on several tectonic plates, making it strange how so many Japanese live with an earthquake risk and a potential for millions to die even with the technology that Japan has in place today. Japan is often criticised because of how few Japanese farmers and farms there are however there is a lack to what they can grow in Japan and in the past their diet consists of fish and vegetables and fruit there was they tend to rely heavily on imports.
Japan is in stage 5 on the DTM was taken from www.populationeducation.org n “Stage 5 of the DTM a country experiences loss to the overall population as the death rate becomes higher than the birth rate. The negative population growth rate is not an immediate effect, however. Based on demographic momentum, in which total population growth increases even while birth rates decline, it will take a generation or two before a negative population growth rate is observed.” this shows that japan is very developed its literacy rate is at 99% and its female literacy rate is 99% this is another reason to why the fertility rate is so low as women are getting jobs and having children later instead of bringing up children and having children at a low age, females are more likely to get a job with a lower percentage in unemployment 7.1% of females are unemployed while 8.7% of males are unemployed.


No comments:
Post a Comment